Explosive EruptionsA second category of volcanoes are those characterized by explosive eruptions. Explosive eruptions are common to volcanoes with very viscous lava and high amounts of gas under pressure. The viscosity, or stickiness, of the lava relates to the silica content. Magma high in silica is more viscous than lavas low in silica. Explosive eruptions are common to volcanoes along the "Ring of Fire", a string of volcanoes extending from the northwest coast of the United States, up through the Aleutian Islands, and into Japan . As the magma rises through the central vent, it gets stuck and gases build to high pressures until an eruption of great force occurs.
Vast amount of ash and pyroclastic material can be ejected from these kinds of volcanoes. Accompanying many of these eruptions are vast outpourings of noxious gases and fine particulate matter called "Nuees Ardentees" or "glowing clouds or avalanches". These clouds can rush down the flanks of a volcano at speeds reaching 60 mph. Escape from such clouds is virtually impossible (See Volcanic Hazards and Episodes: Mt Pelee.)
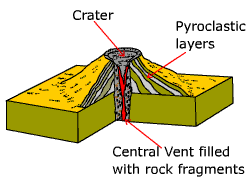
Two types of volcanoes characteristically produce explosive eruptions, cinder cones and
composite volcanoes. Cinder cones are primarily composed of layers of pyroclastic material
built from rock fragments once lodged in the central vent of the volcano
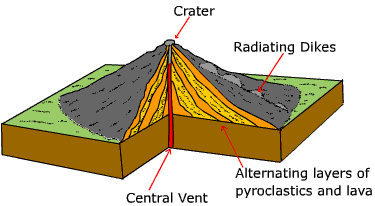
Composite, or stratovolcanoes
also produce explosive eruptions
|
||||
|
|
 Figure 16.11
Mt. St.
Helens, a composite
volcano
Figure 16.11
Mt. St.
Helens, a composite
volcano Figure 16.12 A nearly perfect cinder cone in the Cinder Cones and Lava Beds
Natural Landmark Area in the north-central portion of the Mojave
National Preserve.
Figure 16.12 A nearly perfect cinder cone in the Cinder Cones and Lava Beds
Natural Landmark Area in the north-central portion of the Mojave
National Preserve.